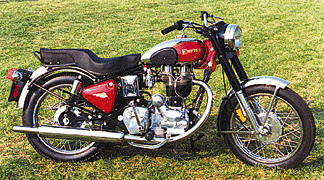
Indian Enfield
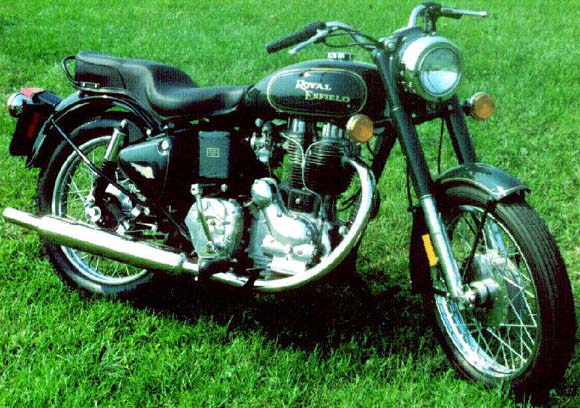
In the 1955 Indian started to import English built motorcycles, and branded them Indian Motorcycles. This was under a five year contract with Royal Enfield, which ran from 1955 – 1959 inclusive. After 1953 the Indian name survived only as the Indian Sales Corporation. The Indian Sales Corporation primarily imported Royal Enfields. These bikes were branded as Indian motorcycles for the American market. The imported motorcycles ranged in size from 150cc to the largest 750cc twin model. One model they imported was the Royal Enfield Bullet. This model was called the Indian Woodsman, and Westerner for the US market. Amazingly this same bike is still in production and is being imported into the United States as the Enfield Bullet.
Now one may ask, how can this be when Royal Enfield went out of business in 1970 ? It is not generally known that the Royal Enfield – after the closure in England – nevertheless went on in another place where the classic already had been manufactured for years. The Royal Enfield was also being manufactured in India. This was owing to the fact that the Indian government had set about purchasing a large number of motorcycles for its police and army in 1955. They needed a solid, economical, maneuverable and reliable motorcycle in order to cope with the miserable roads of the mountainous regions, the heat in the deserts and the humidity of the tropical rain forest. After doing a lot of testing of various brands, the Bullet of the Royal Enfield company was chosen as the most suitable. Thus the Indian government ordered 800 of the 350 cc model in England.
The Royal Enfield company was not able to keep up with the sizable orders coming in from India and a decision was made then to form an independent Indian firm (Enfield India) with British tools in Tiruvottiyur, Madras. There, various Bullet models were manufactured similary to those from England during the 1955 model year. After the closure of the Royal Enfield company, Enfield India was alone in manufacturing the Bullet.
During the 1980’s, the Bullet started being exported to foreign markets, among others, to it’s native country, England, and by the mid 90s the gradually refined classic was for sale in more than 20 countries including Canada and the USA among others. To this day more than half a million Enfields have come out of the modern production line in India, where six different models are being manufactured. On all the models, old traditions like the hand painted golden pinstripes on the tank and the mudguards are maintained. Where on earth did you ever see the like of it?
The Enfield Bullet comes in two versions – a 350 cc and a 500 cc. At the moment Enfield Bullet is available in three variant types: Standard, Deluxe and a Army model. The only difference between the standard and the deluxe models is that the deluxe model has a chrome plated tank, chrome plated mudguards, and chrome air cleaner.
The standard model comes in the colors grey, green, and black. The deluxe model is available in black, red and blue. It is possible to obtain the motorcycle in other colors as well. For both models, an option is available to convert the foot shift to the right side, instead of the British Left Side.
It can be said that everybody stares at the Bullet. Only a few own one. Everywhere you go, you will be turning heads, as people look at your new classic motorcycle. The 1999 Bullet is still a 1955 motorcycle. It’s a rickety ride compared to anything modern. It has huge amounts of character. For just under $4,000, it’s a reasonably priced bike. The Enfield India does have modern hand controls, mirrors, shocks and a seat that works, although, purchasing one of the accessory seats may be more comfortable. The motor is very peppy and has a high amount of torque, for a single. The quality is good, remember they now have 40 years experience building this motorcycle ! Most reviewers relate that overall the bike is very reliable, as well. In an age when we seem fascinated with what is classic, the Royal Enfield works. It’s a classic, hands down. You’ll be the first on the block with one of these. All that is needed, is to add the Indian Script to the tank, and you can claim it is an “Indian Enfield.”
Technical specifications
Engine 4 stroke, air-cooled, OHV
Displacement 499cc
BoreXstroke 84x90mm
Max. bhp 22bhp@5400rpm
Max. torque 3.5 kgm/3000rpm
Compression ratio 6.5:1
Transmission Four-speed gear box
Special features
– Top speed of 125 kmph
– Unique neutral finder lever
– Fuel consumption of 70 mpg
– Stunning black paint finish with gold line on fuel tank
– Tiger-head headlamp casing design
– Pilot lamp for parking
– Unique silencer beat
– Fulcrum lever on main stand for easy parking
– Adjustable rear shock absorbers
For more info please contact the U.S. Distributor:
Classic Motorworks PO BOX 917; Fairbault, MN 55021.
Phone: 800-201-7472. http://www.enfieldmotorcycles.com