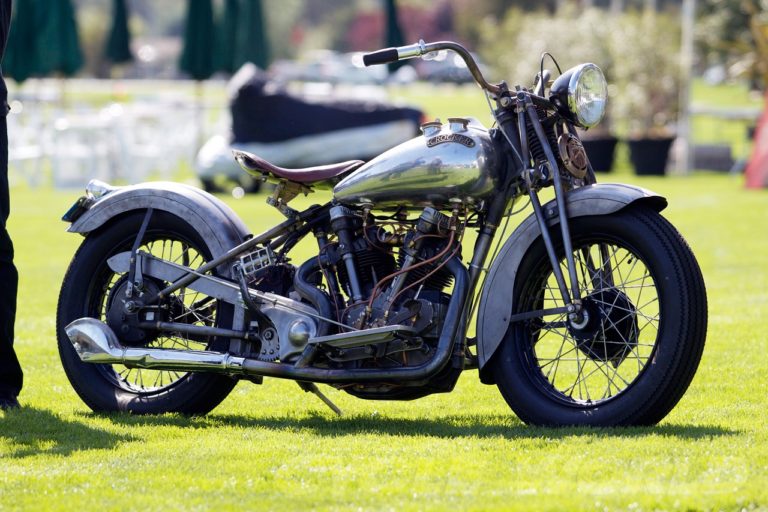
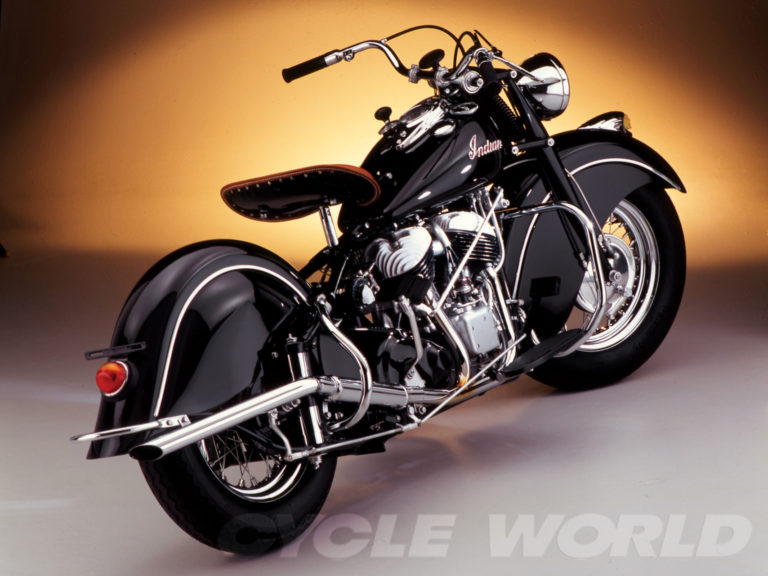
This 1948 Indian Chief is one of the most important Indian motorcycles on the planet.
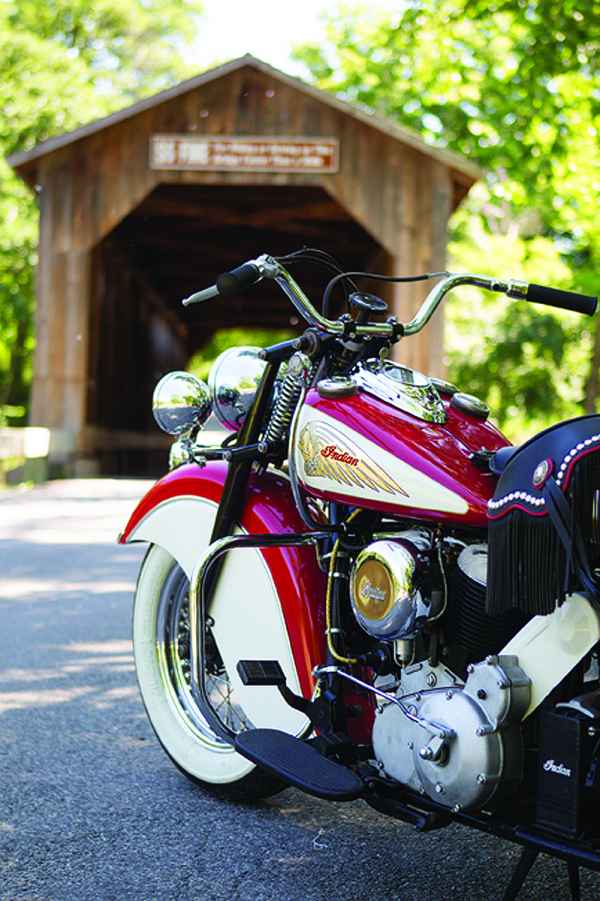
There’s a good chance, many years from now, that history will judge this particular red-and-white 1948 Indian Chief as one of the most important Indian motorcycles on the planet. No, it wasn’t owned by Steve McQueen or any other celebrity; it’s not a special VIN, not the only or the first or the last of anything; it certainly didn’t win any races or set any speed records either. It’s unremarkable except for one fact: This is the motorcycle that spent two years parked in the Polaris design studio, where it served as the visual inspiration and literal touchstone for the design team that reinterpreted the vintage Indian style for the modern era.
This bike isn’t a static showpiece. It’s fully operational, and Indian Product Director Gary Gray offered us the unique opportunity to ride this vintage classic side by side with the modern Chief that carries so much of its DNA in its lines and design. Gray is the person who actually located this bike for Polaris , negotiating the purchase from a Minnesota collector shortly after Polaris acquired the Indian brand in 2011. It’s a 1948 Chief with the mid-level Sportsman trim package, distinguished by the chromed crashbars, handlebar, headlight and spotlights, and “De Luxe” solo saddle. Riding this bike alongside the 2014 Chief Vintage reveals how far bikes have come in 66 years—it feels like light-years—but it’s surprising how similar the two bikes feel in certain ways. That’s a testament to the fine job Gray and company did translating the old glory to a new generation.
The first difference you notice is scale. Wheelbase and seat height are roughly similar, but the vintage bike, weighing just 550 pounds, is almost 250 pounds lighter than the modern machine. This makes the older bike easier to maneuver, especially pushing it around a parking lot, and it handles well at speed too. Sixteen-inch wheels are concealed under those deep fender skirts, and the ride is surprisingly smooth thanks to the coil-sprung, hydraulically damped girder fork and “Double Action” plunger-sprung rear frame (each shock carries two springs: a top spring for cushioning and a bottom spring for damping) that was a cut above Harley’s then-current rigid frame/sprung saddle combination.
The 74ci (1,200cc), 42-degree flathead V-twin, with roots reaching back to 1920, was already obsolete in 1948 (Harley-Davidson released its overhead-valve Panhead that same year), but with roughly 50 hp and a broad spread of torque it’s adequate for back-road cruising. Top speed is said to be near 100 mph, but it’s happier nearer the double nickel where it doesn’t feel (and sound) like it’s going to shake itself apart. Besides, the drum brakes—the front all but useless and the back not much better—can’t compete with more velocity than that.

Often copied, never equaled (until now): the original 1948 Indian Chief
The control layout is utterly unlike the modern bike. Both grips rotate. The right grip “controls” the Linkert carburetor; the left rotates the automotive-type distributor to manually retard or advance the spark for easier starting. “Controls” is in quotes because any grip input to the crude, poorly atomizing Linkert is a mere suggestion. Engine response lags behind grip input by a few seconds, and the lack of a throttle return spring and a solid throttle wire—not a cable—makes rev-matching during shifting all but impossible. Speaking of shifting, there’s no clutch lever. Instead there’s a foot clutch on the left floorboard (a rocker clutch you have to manually engage and disengage, not a spring-loaded “suicide” clutch) and a hand-shifter on the left side of the fuel tank.
Temporarily rewiring your brain to smoothly manipulate that rocker clutch with your foot and fluidly change the cantankerous, non-synchronized, three-speed gearbox with your left hand is the biggest challenge, but once you get the vintage Chief up to speed it’s a delightful back-road ride, with a perfectly upright riding position that’s more natural and less slouchy than the clamshelled hunch the newer bike demands. It’s a classic American motorcycle experience, and Gray and his team have done an excellent job of transposing this vintage vibe onto the new machine. Starting with such sound genetic material as this, though, how could they go wrong?
Source: Hail to the Indian Chief Motorcycle